tbc
Tag: policy effect
Further Development: Recommendations for Action in the Use of Consultation for Mobility Transitions
In a presentation at the Dortmund Conference (dokorp) 2025 “Reasons for planning in time of multiple crisis”, Katharina Holec, Laura Mark and Tobias Escher presented further selected recommendations for dealing with planning conflicts in the context of the transport transition. The presentation arose from the ongoing work on recommendations for action, which was developed by the CIMT research group as a synthesis of the various strands of research and in cooperation with practitioners.
These recommendations are derived from various research findings from the CIMT project. They are based on quantitative data from surveys of more than 2,000 people and qualitative data from more than 20 interviews on various mobility planning processes in three German cities, as well as a quantitative analysis of the participation landscape in Germany based on an extensive database of over 350 transport-related participation processes that we have built up. Following feedback from practitioners, they were revised and put into a coherent form.
Recommendations
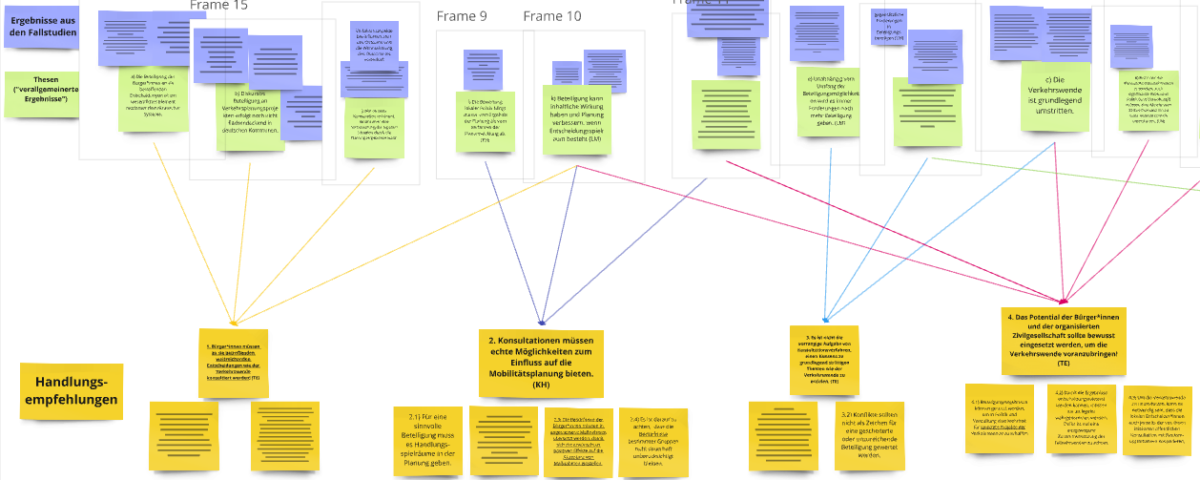
For the presentation, the following two recommendations were selected from those developed to date and presented for discussion:
It is not the primary task of consultation processes to reach a consensus on fundamentally controversial issues such as the mobility transition.
Compared to the presentation at the CMUS conference in Aalborg, this recommendation was slightly adapted and reformulated in the process of developing the recommendations for action, so that consensus is still not seen as the primary task of consultation procedures, but can at least be sought as a partial aspect. Furthermore, it is emphasized that the transport transition is fundamentally controversial. The derivation of the recommendations for action can be found in the contribution to the Mobilities Controversies Conference in Aalborg 2024.
The results of the consultation must be supplemented by other perspectives in order to arrive at a balanced decision in the interests of the mobility transition!
Here, too, the wording was slightly adapted after discussion with practitioners. The wording was changed primarily to make it clear once again that decisions should primarily be made in the interests of the mobility transition and that these should also be balanced for different socio-economic groups.
Presentation and publication
We are currently working on a compilation of these and other empirically based recommendations for the use of participation in the mobility transition.
5th workshop for practitioners on recommendations for action generated from the results
On October 31, November 7 and December 11, workshops for practitioners were held at which we presented recommendations for action and discussed them with the participants. The participants were administrative staff responsible for citizen participation in the various municipalities with which we cooperated and who were involved in the planning and implementation of the participation processes that we examined in our research.
In the course of our investigation of various open consultative participation formats on the topic of urban mobility planning, we were able to generate various findings from which theses can be derived. In a further step, we combined these numerous theses into seven recommendations for action, which are intended to support the implementation of consultative participation formats. At the beginning of the workshops, we used an example to outline the path from insight to recommendations for action before the practitioners themselves got involved and were able to leave comments in our mind map. With the help of digital sticky notes, they added their opinions, additions, criticisms and experiences to the individual recommendations for action. This was followed by discussions on individual recommendations for action. Important points were:
- The usefulness of the recommendations for action in participation practice as tools for classifying one’s own participation
- The usefulness of the recommendations for action in participation practice as an aid to justifying the importance of participation
Overall, the experts agreed that the results of our research are very helpful in communicating the challenges of citizen participation and the resulting consequences to policymakers. In addition, many of the practitioners noted that they found the link to the results of the research clear and structured. Some had the impression that participation and specific consultations are viewed critically in municipal administrations. They share the view that our results can help to train administrative staff and make them aware of the usefulness of participation procedures.
Major points of discussion in the workshops were
- the specificity of the recommendations for action and the inclusion of examples in the presentation of results
- a potentially stronger emphasis on the transparency aspect through the recommendations for action
- an arrangement of the recommendations for action in the chronological order of a participation process
The planners note that the recommendations for action could be made more specific in order to clarify their practical relevance and make them more likely to be applied. In the form in which they were presented, they were rather general and always in strict relation to the results of the research. It was suggested that the recommendations be underpinned with examples from specific participation formats. For example, our research objects could be mentioned, which form the basis of our findings, the theses and thus also the recommendations for action.
Although reformulations and concretizations have been made, examples cannot be found directly in the recommendations. This would have been complicated, especially with regard to the partly abstract quantitative results. However, some examples from the specific participation processes form the basis for the development of the recommendations for action and are sometimes used to underline their importance.
Another aspect that the experts raised is that different tasks and questions arise at different times in a planning process. Some of the seven recommendations for action relate to the planning, implementation or evaluation of the procedures. It was suggested that specific attention should be paid to the participation process and that the recommendations be arranged according to the different stages. This was implemented in the order of the recommendations.
At the end of the workshops, we asked for suggestions for the publication of the results. It was emphasized how important it is for the planners to be able to find these recommendations easily and it was recommended to use existing networks in order to disseminate the results as widely as possible.
We would like to thank the practitioners for their time and important input – and to a large extent for their years of cooperation. We gained many important insights and suggestions that will help us in our work on a helpful and practical publication of recommendations for action.
Addressing Mobilities Controversies through Public Participation?
In a presentation at the C-MUS Congress 2024 in Aalborg (Denmark), Katharina Holec, Laura Mark and Tobias Escher presented selected recommendations for managing planning conflicts in the context of the transport transition.
These recommendations are derived from various research findings from the CIMT project. They are based on quantitative data from surveys of more than 2,000 people and qualitative data from more than 20 interviews on various mobility planning processes in three German cities, as well as a quantitative analysis of the participation landscape in Germany based on an extensive database of over 350 transport-related participation processes that we have compiled.
Recommendations
For the presentation, the following two recommendations were selected from those developed to date and presented for discussion:
It is not the role of a consultation to reach a consensus!
This is derived from the fundamentally conflictual nature of transport planning, which is also reflected in our data and could not be satisfactorily resolved by the participation formats analysed. For example, in the freiRaum Ottensen project, despite extensive participation, 21% of participants were still dissatisfied with the decision made, and 74% of the population were not even aware of the opportunity to participate. This means that the aim should not be to resolve conflicts, but to create a forum for dialogue and the generation of ideas, and that participation should not be judged by the degree of conflict resolution.
Consultation results must be complemented with other perspectives in order to come to a balanced decision!
Participation results can provide a picture of existing concerns and should be taken seriously, but firstly they do not reflect the general mood of the population due to their lack of representativeness, and secondly it cannot be assumed that all important aspects for the mobility transition are included or that mainly supportive contributions are made. This means that consultations should be supplemented by other forms of participation. Participation results should be supplemented and weighed up with other perspectives from different stakeholder spheres and cannot replace a bold political decision.
Presentation and publication
We are currently working on a compilation of these and other empirically based recommendations for the use of participation in the transport transition. This publication will be linked here once it has been finalised. The presentation can be downloaded here:
Results of our research in Hamburg-Ottensen (freiRaum Ottensen): Final presentation
In a joint meeting with representatives of the district office Altona in Hamburg on 7 December 2023, the research group presented the results of the data collection in connection with the freiRaum Ottensen project. FreiRaum Ottensen was one of the five projects in which surveys and interviews were conducted. The focus was on the public consultations in which the general public was able to participate. More information on the project freiRaum Ottensen and the participation formats carried out can be found here.
Selected results
- The population in Ottensen largely perceives a need for improvement in transport and is relatively positive about the transport transition overall.
- Around 50% of the population have heard about the participation process for freiRaum Ottensen, and around 16% have taken part. In comparison with other processes, these are relatively high figures, although the usual over-representation of people with high school diploma, men and older people can be seen despite a wide varieties of participation formats offered to different target groups.
- The discussion during the different participation formats was perceived as constructive and respectful, although conflicts and gaps in the representation of all interests were acknowledged.
- In this project, the policy process was comparatively open to citizens and participants were able to shape the content of the planning outcome.
- For around a third of the population and half of the participants, the participation process had an influence on their satisfaction with the district authority. However, this influence was not always positive: for example, one in four participants was more satisfied with the district authority at the end, but just as many reported less satisfaction.
- Two thirds of the population rated the adopted measures as positive.
- (Statements on the population generally refer to the subgroup of people with a high school diploma – see detailed information on the representativeness of the surveys)
Download
Pushback for the municipal mobility transition? Joint closing event of SÖF Junior Research Groups CIMT and MoveMe on 26th April 2024
The two junior research groups in Social-Ecological Research CIMT and MoveMe held a joint final event showcasing some results of their research into the transition to sustainable mobility. The event took place online on 26. April 2024. More information is available in German.
Inclusivity, transparency and policy effects – procedural justice through participation?
In a presentation at the annual congress of AESOP (Assosiation of European Schools of Planning) in 2023, Katharina Holec, Laura Mark and Tobias Escher presented results from a consultative participation procedure. Key question was whether the procedure could contribute to procedural justice.
Summary
Consultative participation is a frequently used tool to correct traditional inequalities in planning. It is often used to negotiate conflicts relevant to everyday life. Citizens are encouraged to express their interests and ideas. In addition, local administrations expect an increase in legitimacy beliefs among citizens through including them into processes. Procedural justice can be seen as an important aspect of the desired increase in acceptance. The underrepresentation of certain socio-economic groups in the input of consultative participation is one of the main challenges for procedural justice.
Our example is one of the case studies, which we have accompanied scientifically over the last years. Using a mixed methods we investigate the contribution that the procedure makes to procedural justice. We conceptualize this describing the relevance of the aspects inclusivity, transparency and policy effects of a consultative procedure.
Although inclusivity was the declared goal of the organizers it is hardly achieved in the input of the process – that is, in the question of who participates. Things look somewhat more positive when observing the throughput. Discussions were well organized and were also perceived positively by citizens. If we look at the evaluation of the transparency of the process itself, i.e. the throughput, the participants rated it positively. There are limitations in the evaluation of the transparency of the result and the communication after the process. A policy effect exists and is primarily perceived by the participants. However, the policy effect is limited to non-essential issues of the process.
Key findings
- While the consultation process was organized aiming at an overrepresentation of specific marginalized groups, it fails to include lower educated and non-male individuals. The assessment of throughput inclusivity is more positive.
- The consultation process was carried out with timely publication of the results of the individual procedural steps and is also perceived as transparent overall with few differences between different social groups. People with disabilities are somewhat more critical. The assessment of the transparency of the results is somewhat more negative.
- Effects on political decision-making can be found in the fact that the process strengthened and supported the progressive ideas of the administration. Influences of participation existed but were mainly relevant for specific issues, such as the location of bike paths or bus stops not a general direction.
- These effects are more strongly perceived by participants.
Consultation of citizens in mobility projects: The participation landscape at municipal level in Germany
In this article in the journal Raumforschung und Raumordnung, Laura Mark, Katharina Holec and Tobias Escher present the results of a survey on the scope and organisation of consultation in mobility-related municipal planning. From these results, conclusions can be drawn about the participation landscape in Germany.
The results were presented in an earlier version at the 18th annual conference of the Mobility and Transport Working Group (AK MoVe) in June 2023.
Abstract
Municipalities as key actors in the transport transition are increasingly using consultative public participation in planning. So far, however, it is unclear to what extent they use participatory processes in mobility-related planning and how these are designed. Given the challenges associated with the transition to a climate-neutral transport system, taking stock of existing efforts is highly relevant in order to assess the practical significance of participation processes and to better investigate the role of different types of procedures and contexts.
This study fills this gap based on an analysis of the consultative, discursive participation processes for mobility-related planning in German cities since 2015. The study examined ‘participation-oriented’ cities with guidelines for citizen participation, which were compared to a random selection of ‘typical’ municipalities in North Rhine-Westphalia, Baden-Württemberg and Saxony as well as the three German city states.
Based on these approximately 180 cities and 350 procedures, it becomes clear that discursive consultations are carried out regularly, in particular in municipalities with guidelines and larger cities. Worth criticizing is that the formats used can usually reach only certain groups of the population and that for a significant proportion of the processes examined no information on the results of participation can be found. This means that the potentials of discursive citizen participation in addressing the municipal transport transition have not yet been sufficiently utilised.
Key Findings
- Participation in municipal planning procedures related to mobility is no longer an exception, but not yet the rule either. Based on the data of our sample, it can be presumed that in most municipalities in Germany there was no possibility to participate in such procedures in the period under consideration.
- In general, cities with guidelines involved their citizens more frequently, more often and with more diverse topics and formats. Medium-sized and large cities consulted their citizens significantly more often than small towns.
- Weaknesses are evident in the participation formats used: The majority of municipalities relied on self-selected selection processes. First attempts with target group-specific formats or random selection can be found mainly in the municipalities with guidelines and in the city states. A large proportion of the procedures were also carried out purely online.
- For 5 to 10% of the procedures, no current status could be found, and for a larger proportion it was unclear what happened after the consultation. This is true for all municipalities, although less so for those with guidelines, and can be regarded as a lack of transparency and impact of participation.
Publication
Mark, Laura; Holec, Katharina; Escher, Tobias (2024): Die Beteiligung von Bürgerinnen und Bürgern bei kommunalen Mobilitätsprojekten: Eine quantitative Erhebung konsultativer Beteiligungsverfahren in Deutschland. In: RuR (Spatial Research and Planning). DOI: 10.14512/rur.2239
Database
The database, i.e. the systematically collected compilation of the participation processes and their coding according to specific aspects, can be researched and downloaded here.
Mobility Transition through Participation? Policy impact of discursive, consultative public participation on urban transport projects for sustainability
Dissertation Projekt, Laura Mark
In my dissertation project at the Faculty of Architecture at RWTH Aachen University, I am using two case studies to investigate the substantive impact of consultative public participation on political decisions and the implications for sustainable development. My object of investigation is planning for the sustainable mobility transition, since on the one hand it is important and urgent for sustainable development and on the other hand it directly affects people’s everyday lives and thus often leads to resistance.
Abstract
A socio-ecological shift in transport requires profound changes in public space that affect the daily lives of users. This redistribution of road space and change in conditions of use is primarily carried out through spatial planning on the part of the public sector, in which the public is also increasingly involved. This is usually associated (implicitly or explicitly) with the public having an influence on the content of the planning; however, the actual effect has hardly been researched.
I am investigating the mechanisms through which the substantive impact of public participation comes about or is prevented, and which factors influence these mechanisms. I am interested in the conditions under which these substantive effects contribute to integrated transport planning, measured both in terms of democratic theory and substantive criteria.
Two municipal transport transition projects in Hamburg serve as case studies, in which the public can participate or has participated through consultation offers and other forms of participation: the redesign of the Elbchaussee in Hamburg and the low-car design of the Ottensen neighbourhood in Hamburg. The processes differ, among other things, in their framework conditions, spatial scale, tasks and participation offerings. For the detailed reconstruction and analysis of these processes, I mainly rely on data from qualitative interviews, document and media analyses, supplemented by results of quantitative population and participant surveys.
Expected Results
Expected results are theses on public participation in the context of the mobility transition. These deal with the mechanisms and factors that influence policy impact and come about through a detailed analysis of the individual case studies, a targeted comparison of the two case studies with each other and the embedding of the empirical results in the state of research as well as other results from the project. These theses are intended to contribute to the discussion on the role of the public in the context of a socio-ecological transformation.
Socio-spatial justice through public participation?
In this presentation at the AESOP (Assosiation of European Schools of Planning) annual Congress in 2022, Laura Mark, Katharina Huseljić and Tobias Escher introduced a framework of distributive socio-spatial justice and the way consultation procedures can contribute, before evaluating the case study Elbchaussee in Hamburg regarding socio-spatial justice, using qualitative and quantitative results.
Abstract
Our current transport system exhibits significant socio-spatial injustices as it has both major negative environmental effects and structurally disadvantages certain socio-economic groups. Planning processes increasingly include elements of public participation, often linked to the hope of better understanding and integrating different mobility needs into the planning process. However, so far there is little knowledge on whether public participation results indeed in more socio-spatial justice.
To approach this question, we focus on socio-spatial justice as distributive justice and investigate how well consultative planning procedures do actually lead to measures that both contribute to sustainability (i.e. reduce or redistribute negative external effects) and cater for the needs of disadvantaged groups (e.g. those with low income or education, women and disabled people). To this end, we have investigated in detail the case study of the reconstruction of the Elbchaussee, a representative main road of citywide importance in the district of Altona in Hamburg, Germany. We are drawing on both qualitative and quantitative data including expert interviews and public surveys.
We first show that the process did result in planning measures that contribute slightly to ecological sustainability. Second, in particular through improving the situation for pedestrians and cyclists as well as the quality of stay, the measures should contribute to more justice for some groups but this is recognized only by non-male groups. Beyond this there are no effects for people with low income, low education, those with mobility restrictions or with particular mobility needs often associated with these groups. Overall, we conclude that the consultative planning process provides only a small contribution to socio-spatial justice and we discuss potential explanations.
Key Findings
- The consultative planning process as a whole resulted in measures that contribute slightly to socio-spatial justice, since they support the transition to more sustainable mobility and will benefit some disadvantages groups, though both to a limited degree.
- We find that the consultation procedure had no significant influence on the policy. In terms of socio-spatial justice, no positive effects can be traced back to the consultation procedure. Notably, those that participated in the consultation did indeed report less satisfaction with the measures.
- We trace those limited contributions back to some general features of consultation and the current planning system, but also find that in the case study the scope of possible influence was very limited due to external restrictions and power imbalances.
Publication
We are working on a publication for a peer-reviewed journal. The publication will be linked here as soon as it is published.