tbc
Category: practitioners
Results of our surveys in Marburg (MoVe 35): Final presentation
As part of a joint digital exchange with the city administration of the city of Marburg (including citizen participation and transport planning) on September 25, 2024, the research group presented the results of the surveys in connection with the participation process for the MoVe 35 mobility and transport concept. The MoVe 35 project was one of a total of five planning projects that were intensively investigated by the CIMT research group over several years in order to examine the effects of consultative citizen participation on political attitudes, among other things.
Various participation formats were carried out as part of the planning process, e.g. an online survey, workshops, a project advisory board and an online dialog on public transport. A (council) referendum was also held in connection with the mobility concept. Further information on the MoVe 35 project and the participation formats used can be found on the city of Marburg’s website.
This planning and participation process was examined by the CIMT research group at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf independently (i.e. without being commissioned or influenced by the city of Marburg), primarily with the help of surveys of Marburg residents. For this purpose, a randomly selected part of the population in Marburg was surveyed in 2021 and 2024. Further information on the research group’s surveys can be found here.
Selected results
- As in all of our project areas, transport policy and the transport transition are conflicting issues. In Marburg, however, there is a particularly clear contrast between the educational groups. For example, the majority of people without a high school diploma reject the idea of reducing space for car traffic in the future, while almost half of those with a high school diploma can imagine doing so.
- Supporters and opponents of the mobility transition were similarly represented in the participation process. It was noticeable that an above-average number of car drivers took part in Marburg.
- The measures envisaged as part of Move 35 are viewed positively by the majority of people with high education in order to achieve the goals of sustainable mobility – in contrast to people without high education.
- The very different assessments of the two educational groups are also evident in the (planned) voting behavior for the referendum on halving car traffic: the majority of people with high education are in favor, the majority of people with low education are against, and participants in the consultation process are divided.
- Although satisfaction with the local institutions (mayor, city administration, council) was slightly better overall than in other project areas, it deteriorated significantly between 2021 and 2024 among people with low education.
- The information on the participation process reached a large part of the population. Nevertheless, it was mainly highly educated middle-aged men who took part – typical of consultative participation. It had a relatively large impact on citizens’ satisfaction with the mayor, administration and council. As expected, people who welcome the measures of MoVe 35 tend to be more satisfied, while those who reject the measures express greater dissatisfaction.
Download presentation
A prepared form of the results presentation can be downloaded here:
Results of our surveys in Offenburg (OG 2035): Final presentation
In a joint meeting with representatives from the city of Offenburg’s urban development and transport planning departments on October 11, 2024, the research group presented the results of the surveys conducted in connection with the participation process for the OG 2035 Transport Master Plan. The Transport Master Plan OG 20235 was one of a total of five planning projects that the CIMT research group studied intensively over several years in order to investigate the effects of consultative citizen participation on political attitudes, among other things.
Various formats were carried out as part of the planning process, e.g. online dialogs, workshops, local forums, youth participation and the establishment of pop-up measures. Further information on the OG 2035 project and the participation formats carried out can be found on the City of Offenburg website.
This planning and participation process was examined by the CIMT research group at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf independently (i.e. without being commissioned or influenced by the city of Offenburg), primarily with the help of surveys of Offenburg residents. For this purpose, a randomly selected part of the population in Offenburg was surveyed in 2021 and 2023. Further information on the research group’s surveys can be found here.
Selected results
- Transport policy and the transport transition are conflicting issues in Offenburg – just like in all other project areas examined. All opinions were represented in the participation process, although those in favor of the mobility transition were somewhat stronger and car users were also less common.
- Satisfaction with the local institutions (mayor, city administration, council) is rather average overall (and slightly worse than in other project areas) and deteriorated significantly from 2021 to 2023 in particular.
- The transport measures adopted as part of the OG 2035 master plan do not satisfy all interests, but overall only a minority (20-25%) are really against them. People who took part in the participation process rate the results more positively overall.
- As with most open participation formats, the participants are not representative of the population. They are mainly people with a high school diploma, middle-aged people and men.
- The participation process had a (comparatively low) and overall negative influence on satisfaction with local politics and administration, whereby the city administration was rated more positively than the mayor and council, especially by the consultation participants. As expected, people who welcome the measures of OG 2035 tend to be more satisfied, while those who reject the measures express greater dissatisfaction.
Download presentation
Results of our surveys in Marburg (MoVe 35): Final presentation
As part of a joint digital exchange with the city administration of the city of Marburg (including citizen participation and transport planning) on September 25, 2024, the research group presented the results of the surveys in connection with the participation process for the MoVe 35 mobility and transport concept. The MoVe 35 project was one of a total of five planning projects that were intensively investigated by the CIMT research group over several years in order to examine the effects of consultative citizen participation on political attitudes, among other things.
Various participation formats were carried out as part of the planning process, e.g. an online survey, workshops, a project advisory board and an online dialog on public transport. A (council) referendum was also held in connection with the mobility concept. Further information on the MoVe 35 project and the participation formats used can be found on the city of Marburg’s website.
This planning and participation process was examined by the CIMT research group at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf independently (i.e. without being commissioned or influenced by the city of Marburg), primarily with the help of surveys of Marburg residents. For this purpose, a randomly selected part of the population in Marburg was surveyed in 2021 and 2024. Further information on the research group’s surveys can be found here.
Selected results
- As in all of our project areas, transport policy and the transport transition are conflicting issues. In Marburg, however, there is a particularly clear contrast between the educational groups. For example, the majority of people without a high school diploma reject the idea of reducing space for car traffic in the future, while almost half of those with a high school diploma can imagine doing so.
- Supporters and opponents of the mobility transition were similarly represented in the participation process. It was noticeable that an above-average number of car drivers took part in Marburg.
- The measures envisaged as part of Move 35 are viewed positively by the majority of people with high education in order to achieve the goals of sustainable mobility – in contrast to people without high education.
- The very different assessments of the two educational groups are also evident in the (planned) voting behavior for the referendum on halving car traffic: the majority of people with high education are in favor, the majority of people with low education are against, and participants in the consultation process are divided.
- Although satisfaction with the local institutions (mayor, city administration, council) was slightly better overall than in other project areas, it deteriorated significantly between 2021 and 2024 among people with low education.
- The information on the participation process reached a large part of the population. Nevertheless, it was mainly highly educated middle-aged men who took part – typical of consultative participation. It had a relatively large impact on citizens’ satisfaction with the mayor, administration and council. As expected, people who welcome the measures of MoVe 35 tend to be more satisfied, while those who reject the measures express greater dissatisfaction.
Download presentation
A prepared form of the results presentation can be downloaded here:
Further Development: Recommendations for Action in the Use of Consultation for Mobility Transitions
In a presentation at the Dortmund Conference (dokorp) 2025 “Reasons for planning in time of multiple crisis”, Katharina Holec, Laura Mark and Tobias Escher presented further selected recommendations for dealing with planning conflicts in the context of the transport transition. The presentation arose from the ongoing work on recommendations for action, which was developed by the CIMT research group as a synthesis of the various strands of research and in cooperation with practitioners.
These recommendations are derived from various research findings from the CIMT project. They are based on quantitative data from surveys of more than 2,000 people and qualitative data from more than 20 interviews on various mobility planning processes in three German cities, as well as a quantitative analysis of the participation landscape in Germany based on an extensive database of over 350 transport-related participation processes that we have built up. Following feedback from practitioners, they were revised and put into a coherent form.
Recommendations
For the presentation, the following two recommendations were selected from those developed to date and presented for discussion:
It is not the primary task of consultation processes to reach a consensus on fundamentally controversial issues such as the mobility transition.
Compared to the presentation at the CMUS conference in Aalborg, this recommendation was slightly adapted and reformulated in the process of developing the recommendations for action, so that consensus is still not seen as the primary task of consultation procedures, but can at least be sought as a partial aspect. Furthermore, it is emphasized that the transport transition is fundamentally controversial. The derivation of the recommendations for action can be found in the contribution to the Mobilities Controversies Conference in Aalborg 2024.
The results of the consultation must be supplemented by other perspectives in order to arrive at a balanced decision in the interests of the mobility transition!
Here, too, the wording was slightly adapted after discussion with practitioners. The wording was changed primarily to make it clear once again that decisions should primarily be made in the interests of the mobility transition and that these should also be balanced for different socio-economic groups.
Presentation and publication
We are currently working on a compilation of these and other empirically based recommendations for the use of participation in the mobility transition.
5th workshop for practitioners on recommendations for action generated from the results
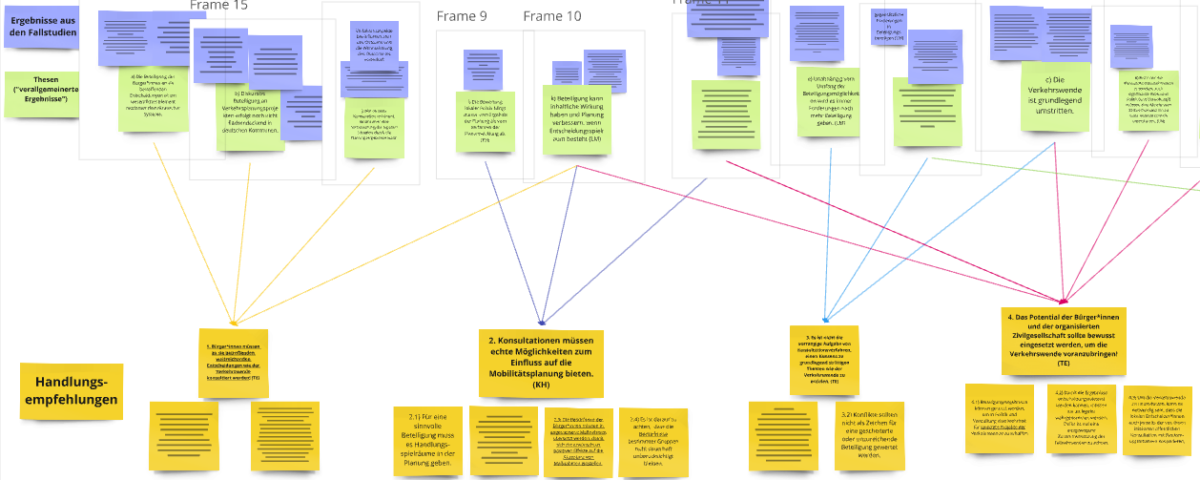
On October 31, November 7 and December 11, workshops for practitioners were held at which we presented recommendations for action and discussed them with the participants. The participants were administrative staff responsible for citizen participation in the various municipalities with which we cooperated and who were involved in the planning and implementation of the participation processes that we examined in our research.
In the course of our investigation of various open consultative participation formats on the topic of urban mobility planning, we were able to generate various findings from which theses can be derived. In a further step, we combined these numerous theses into seven recommendations for action, which are intended to support the implementation of consultative participation formats. At the beginning of the workshops, we used an example to outline the path from insight to recommendations for action before the practitioners themselves got involved and were able to leave comments in our mind map. With the help of digital sticky notes, they added their opinions, additions, criticisms and experiences to the individual recommendations for action. This was followed by discussions on individual recommendations for action. Important points were:
- The usefulness of the recommendations for action in participation practice as tools for classifying one’s own participation
- The usefulness of the recommendations for action in participation practice as an aid to justifying the importance of participation
Overall, the experts agreed that the results of our research are very helpful in communicating the challenges of citizen participation and the resulting consequences to policymakers. In addition, many of the practitioners noted that they found the link to the results of the research clear and structured. Some had the impression that participation and specific consultations are viewed critically in municipal administrations. They share the view that our results can help to train administrative staff and make them aware of the usefulness of participation procedures.
Major points of discussion in the workshops were
- the specificity of the recommendations for action and the inclusion of examples in the presentation of results
- a potentially stronger emphasis on the transparency aspect through the recommendations for action
- an arrangement of the recommendations for action in the chronological order of a participation process
The planners note that the recommendations for action could be made more specific in order to clarify their practical relevance and make them more likely to be applied. In the form in which they were presented, they were rather general and always in strict relation to the results of the research. It was suggested that the recommendations be underpinned with examples from specific participation formats. For example, our research objects could be mentioned, which form the basis of our findings, the theses and thus also the recommendations for action.
Although reformulations and concretizations have been made, examples cannot be found directly in the recommendations. This would have been complicated, especially with regard to the partly abstract quantitative results. However, some examples from the specific participation processes form the basis for the development of the recommendations for action and are sometimes used to underline their importance.
Another aspect that the experts raised is that different tasks and questions arise at different times in a planning process. Some of the seven recommendations for action relate to the planning, implementation or evaluation of the procedures. It was suggested that specific attention should be paid to the participation process and that the recommendations be arranged according to the different stages. This was implemented in the order of the recommendations.
At the end of the workshops, we asked for suggestions for the publication of the results. It was emphasized how important it is for the planners to be able to find these recommendations easily and it was recommended to use existing networks in order to disseminate the results as widely as possible.
We would like to thank the practitioners for their time and important input – and to a large extent for their years of cooperation. We gained many important insights and suggestions that will help us in our work on a helpful and practical publication of recommendations for action.
Sustainable mobility and housing for families (in Düsseldorf)
In this presentation for the Düsseldorfer Familientisch, a network of various stakeholders in Düsseldorf, Tobias Escher explained why mobility and housing are closely linked. A transformation of the current car-centred mobility system is doomed to fail without a simultaneous change in housing policy – and not just in cities. He began by explaining that sustainable mobility is more than just making transport more environmentally friendly, but also targets traffic noise and road safety. Using the example of housing for families, he showed how their concerns and needs differ greatly between those who live in urban centres and families who settle in the proverbial ‘little house in the country’. For both groups, he presented a range of measures that can be used to promote more sustainable mobility options. These range from promoting opportunities for working and shopping nearby to more appropriate pricing of public space.
The event took place on 12 June 2024. There is more information available from the official record of the event.
Results of our research in Hamburg-Ottensen (freiRaum Ottensen): Final presentation
In a joint meeting with representatives of the district office Altona in Hamburg on 7 December 2023, the research group presented the results of the data collection in connection with the freiRaum Ottensen project. FreiRaum Ottensen was one of the five projects in which surveys and interviews were conducted. The focus was on the public consultations in which the general public was able to participate. More information on the project freiRaum Ottensen and the participation formats carried out can be found here.
Selected results
- The population in Ottensen largely perceives a need for improvement in transport and is relatively positive about the transport transition overall.
- Around 50% of the population have heard about the participation process for freiRaum Ottensen, and around 16% have taken part. In comparison with other processes, these are relatively high figures, although the usual over-representation of people with high school diploma, men and older people can be seen despite a wide varieties of participation formats offered to different target groups.
- The discussion during the different participation formats was perceived as constructive and respectful, although conflicts and gaps in the representation of all interests were acknowledged.
- In this project, the policy process was comparatively open to citizens and participants were able to shape the content of the planning outcome.
- For around a third of the population and half of the participants, the participation process had an influence on their satisfaction with the district authority. However, this influence was not always positive: for example, one in four participants was more satisfied with the district authority at the end, but just as many reported less satisfaction.
- Two thirds of the population rated the adopted measures as positive.
- (Statements on the population generally refer to the subgroup of people with a high school diploma – see detailed information on the representativeness of the surveys)
Download
AI for the evaluation of participation? The potential of language models to recognise modes of transport in participation contributions
In this article in the journal Internationales Verkehrswesen, Laura Mark, Julia Romberg and Tobias Escher present a language model that can be used to reliably recognise modes of transport in participation contributions. They show that supervised machine learning can usefully support the evaluation of participation contributions in mobility-related online participation processes.
Summary
Consultations are an important part of transport planning and can help to integrate knowledge from the public into the planning process. However, online formats in particular often result in large volumes of contributions, the thorough evaluation of which is resource-intensive. It is hoped that the use of AI will support this.
The language model presented in this article is based on the concept of supervised machine learning for text classification. Pre-trained models are re-fined using smaller data sets. In this way, a model can be adapted to a specific area of application, such as mobility-related consultation processes.
A pre-trained German-language version of the high-performance RoBERTa language model was used as a starting point. Using a categorisation scheme that mainly distinguishes between the modes of transport mentioned, 1,700 contributions from seven transport planning consultation processes were manually coded. The resulting data was used partly as training data for fine-tuning the language model and partly for evaluation.
Results
- Overall, it was shown that language models already available today are suitable for supporting the evaluation of consultation processes in practice. The language model developed here for recognising the modes of transport can serve as the basis for a specific application in municipal planning practice.
- The post-trained RoBERTa language model is very effective at assigning the appropriate modes of transport. The model presented by us can always reliably assign well over 90% of the entries correctly to the modes of transport they contain.
- For the processes on whose contributions the model had been trained, an average of 97% of the categories could be correctly assigned (on a separate test set). For contributions from other transport-related participation procedures, the appropriate modes of transport could still be assigned very reliably with an accuracy of 91 to 94%.
- The performance of the model therefore hardly deteriorates when it is applied to previously unknown data from mobility-related participation procedures. This means that manual coding in advance can be omitted, at least for similarly structured participation procedures, which significantly reduces the effort involved.
Publication
Mark, Laura; Romberg, Julia; Escher, Tobias (2024): KI zur Auswertung von Beteiligung. In: Internationales Verkehrswesen 76 (1), S. 12–16. DOI: 10.24053/iv-2024-0003
The political shaping of the sustainability transformation: participatory and ecological?
In this article in regierungsforschung.de, the academic online magazine of the NRW School of Governance, Tobias Escher explores the question of whether the participation formats required for a participatory development of the transformation to a more sustainable society can also be implemented in an ecologically sustainable manner. In other words, the question is how the principle of (ecologically) sustainable governance can be upheld in the democratically important area of political participation.
Abstract
The transformation to a sustainable society can only succeed through the involvement of all stakeholders. At the same time, sustainable governance requires that these participation processes also fulfil the requirements of sustainability. Based on a systematic discussion of the greenhouse gas emissions generated by various political participation formats, this article argues that in view of the functional and normative significance of political participation, its environmental footprint does usually not contradict the demand for sustainable governance.
Key findings
- The implementation of participation formats generates greenhouse gas emissions due to the energy required, the mobility of the participants and, where applicable, catering and accommodation. Crucially, the level of emissions depends on whether the formats are held in person or digitally (see table below).
- For local face-to-face formats, the emissions from the event venue and mobility of participants are comparatively low and only amount to around 2kg of CO2-equivalents per person in the scenario analysed. The emissions increase considerably as soon as participants have to travel further (using fossil-fuelled transport) – in the underlying scenario by a factor of twelve to 24kg. This is roughly equivalent to the average emissions from a 100km car journey.
- In contrast, online participation formats only generate very low emissions (around 0.3kg per person in the scenario). Nevertheless, the choice of participation formats cannot be based solely on their short-term ecological costs, but must also take into account normative requirements for inclusion and popular control. Digital participation formats in particular represent significant barriers to participation for already disadvantaged population groups (see also our DigiBeSt-report).
- Overall, participation has an ecological footprint, but this is generally justified by functional and normative considerations because after all, governance should not only be sustainable, but above all democratic!
| | face-to-face participation | digital participation | ||
| | local | (inter)-regional | asynchron | synchron |
| energy | heating & climatisation of event venue | operation of end user devices & data centres | more data intensive communication | |
| mobility | travel | travel | not applicable | |
| catering & accommodation | catering | accommodation | not applicable | |
Publication
Escher, Tobias (2024): Die politische Gestaltung der Nachhaltigkeitstransformation: partizipativ und ökologisch? Essay. In: Regierungsforschung.de (15. Jahrgang). https://regierungsforschung.de/die-politische-gestaltung-der-nachhaltigkeitstransformation-partizipativ-und-oekologisch/